Abstract
Case Report
Septic Shock on Bartholinitis: Case Report and Modern Surgical Approaches
Oumaima Fakir*, Hanaa Lazhar, Aziz Slaoui, Amina Lakhdar and Aziz Baydada
Published: 07 March, 2025 | Volume 8 - Issue 1 | Pages: 015-018
Bartholinitis, or Bartholin's gland abscess, is a relatively common gynecological condition among women of reproductive age. Its annual incidence is estimated at approximately 0.5 per 1,000 women, which corresponds to a lifetime cumulative risk of about 2%. The condition primarily affects patients between 20 and 50 years old, with a peak frequency observed between 35 and 50 years.
After menopause, due to the natural involution of the gland, Bartholin's cysts and abscesses become less frequent, although they can still occur. Moreover, in women over 50, the appearance of a new mass in the gland region should prompt caution, as it may, in rare cases, indicate a carcinoma of the Bartholin's gland or an adjacent vulvar cancer. Therefore, for patients over 40 presenting with a newly emerged cyst or abscess, clinical guidelines recommend performing a biopsy or excision to rule out malignancy.
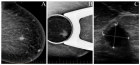
We present the case of a 50-year-old woman with no significant medical history, who was urgently referred to the gynecological emergency department due to confusion, unexplained fever of 40 °C, and resistant leucorrhoea following a week of corticosteroid antibiotic therapy. Clinical examination revealed a large, tender right vulvar mass, indicative of an acute
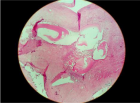
Bartholin's abscess. The patient exhibited signs of septic shock and was admitted to the ICU. Following a diagnosis of sepsis, broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy was initiated, alongside fluid resuscitation and norepinephrine support. Surgical drainage of the abscess confirmed the presence of E. coli. The patient's condition improved rapidly, and she was discharged on postoperative day 8 with no complications.
This case underscores that while Bartholin's abscess is typically benign, severe complications, including septic shock, can occur—especially in patients over 50. The appearance of a new Bartholin's region mass in older women should prompt consideration of malignancy, necessitating biopsy or excision. Recent studies compare various therapeutic approaches including simple incision and drainage, Word catheter placement, marsupialization, silver nitrate application, and complete gland excision. Each method has its advantages and drawbacks, with marsupialization offering lower recurrence rates and higher patient satisfaction in many instances.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001183 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Abscess; Post-menopausal; Malignancy
References
- Das S, Shil R, Dhanpal HN. Bartholin gland cyst and abscess: an updated scenario. International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences. 2024;12(1). Available from: https://doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20234030
- Kilpatrick C. Bartholin gland cyst and bartholin gland abscess [Internet]. MSD Manual Professional Edition. 2023. Available from: https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/gynecology-and-obstetrics/miscellaneous-gynecologic-disorders/bartholin-gland-cyst-and-bartholin-gland-abscess
- Visco AG, Del Priore G. Postmenopausal bartholin gland enlargement: a hospital-based cancer risk assessment. Obstet Gynecol. 1996;87(2):286-90. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/0029-7844(95)00404-1
- Goklu MR, Tunc S, Andan C, Aksin S. Approach to Bartholin's abscesses and recurrences under office conditions. J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod. 2021;50(9):102186. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jogoh.2021.102186
- Lee WA, Wittler M. Bartholin Gland Cyst. [Updated 2023 Jul 5]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. 2025. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532271/
- Karabük E, Ganime Aygün E. Marsupialization versus Word catheter in the treatment of Bartholin cyst or abscess: retrospective cohort study. J Turk Ger Gynecol Assoc. 2022;23(2):71-74. Available from: https://doi.org/10.4274/jtgga.galenos.2022.2022-1-6
- Wechter R, Frawley D. Postmenopausal Bartholin Gland Enlargement: Cancer Risk Assessment. Obstetrics & Gynecology. 1995;85(6):1049-1054.
- Sinha A. Management of Bartholin Gland Cyst and Abscess, Gynae Professional Forum Obstetrics and Gynaecology Directorate. S Powell Gynae SPR 10/1/2023 ver2. Available from: https://wisdom.nhs.wales/health-board-guidelines/guidelines-by-health-board/cardiff-vale/cardiff-vale-gynaecology-guidelines/bartholin-gland-cyst-abscess-management-of-cvg-guideline-2022-pdf/
- Word catheter for Bartholin’s abscess [Internet]. Chelsea and Westminster Hospital NHS Foundation Trust. Available from: https://www.chelwest.nhs.uk/your-visit/patient-leaflets/womens-services/word-catheter-for-bartholins-abscess
- Shearin RS, Boehlke J, Karanth S. Toxic shock-like syndrome associated with Bartholin's gland abscess: case report. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1989;160(5 Pt 1):1073-4. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(89)90163-4
- Courtney-Brooks M, Scalici J, Henretta MS, Modesitt SC, Jazaeri AA, Cantrell LA, et al. Vulvar necrotizing soft tissue infection: A review of a multi-disciplinary surgical emergency and management in the modern era. Gynecol Oncol Case Rep. 2013;5:6-9. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gynor.2013.02.002
Figures:
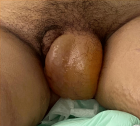
Figure 1
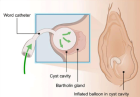
Figure 2
Similar Articles
-
Gynaecological malignancies after breast cancer diagnosis: A population-based studyMaria Pilar Barretina-Ginesta,Jaume Galceran*,Helena Pla,Cristina Meléndez,Anna Carbo Bague,Alberto Ameijide,Marià Carulla,Jordi Barretina,Angel Izquierdo,Rafael Marcos-Gragera. Gynaecological malignancies after breast cancer diagnosis: A population-based study. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001031; 2: 113-118
-
Endometriosis as a risk factor for colorectal cancerVíctor Manuel Vargas-Hernández*,José María Tovar- Rodríguez,Víctor Manuel Vargas-Aguilar . Endometriosis as a risk factor for colorectal cancer. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001057; 3: 093-097
-
A rare case of giant ovarian serous cystadenoma presenting as psuedo-meigs syndromeRichmond Ronald Gomes*,Sayeda Noureen,Habiba Akhter. A rare case of giant ovarian serous cystadenoma presenting as psuedo-meigs syndrome. . 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001078; 4: 010-014
-
Leiomyosarcoma in pregnancy: Incidental finding during routine caesarean sectionToon Wen Tang*,Phoon Wai Leng Jessie. Leiomyosarcoma in pregnancy: Incidental finding during routine caesarean section. . 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001094; 4: 092-095
-
A Genetic study in assisted reproduction and the risk of congenital anomaliesKaparelioti Chrysoula,Koniari Eleni*,Efthymiou Vasiliki,Loutradis Dimitrios,Chrousos George,Fryssira Eleni. A Genetic study in assisted reproduction and the risk of congenital anomalies. . 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001095; 4: 096-100
-
Cervical choriocarcinoma in a post-menopause woman: Case report and review of literatureZeinab Nazari,Leila Mortazavi*,Noushin Gordani. Cervical choriocarcinoma in a post-menopause woman: Case report and review of literature. . 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001101; 5: 019-021
-
Cost-analysis comparison of clinical risk assessment with and without ROMA for the management of women with pelvic massesKaylee A Underkofler,Alexandra J Morell,Rianne Esquivel,Francesca I DeSimone,M Craig Miller,Richard G Moore*. Cost-analysis comparison of clinical risk assessment with and without ROMA for the management of women with pelvic masses. . 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001112; 5: 080-089
-
Meigs syndrome: About an uncommon case reportAziz Slaoui*,Hanaa Lazhar,Noha Amail,Najia Zeraidi,Amina Lakhdar,Aicha Kharbach,Aziz Baydada. Meigs syndrome: About an uncommon case report. . 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001120; 6: 010-013
-
High-Grade Endometrial Mesenchymal Sarcoma: Current Status and Future TrendsLushuang Zhang, Liubiqi Zhao*. High-Grade Endometrial Mesenchymal Sarcoma: Current Status and Future Trends. . 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001141; 6: 132-134
-
Fibrothecal Tumors of the Ovary - Case ReportM Lamrani*,K Lakhdar,S Sardaoui,Y Alami,F Tijami,H Hachi,Z El-Hanchi,A Baydada. Fibrothecal Tumors of the Ovary - Case Report. . 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001177; 7: 117-119
Recently Viewed
-
Clinical and Histopathological Mismatch: A Case Report of Acral FibromyxomaMonica Mishra*,Kailas Mulsange,Gunvanti Rathod,Deepthi Konda. Clinical and Histopathological Mismatch: A Case Report of Acral Fibromyxoma. Arch Pathol Clin Res. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.apcr.1001045; 9: 005-007
-
Unconventional powder method is a useful technique to determine the latent fingerprint impressionsHarshita Niranjan,Shweta Rai,Kapil Raikwar,Chanchal Kamle,Rakesh Mia*. Unconventional powder method is a useful technique to determine the latent fingerprint impressions. J Forensic Sci Res. 2022: doi: 10.29328/journal.jfsr.1001035; 6: 045-048
-
Doppler Evaluation of Renal Vessels in Pediatric Patients with Relapse and Remission in Different Categories of Nephrotic SyndromeAmit Nandan Dhar Dwivedi*, Srishti Sharma, OP Mishra, Girish Singh. Doppler Evaluation of Renal Vessels in Pediatric Patients with Relapse and Remission in Different Categories of Nephrotic Syndrome. J Clini Nephrol. 2023: doi: 10.29328/journal.jcn.1001112; 7: 067-072
-
Atlantoaxial subluxation in the pediatric patient: Case series and literature reviewCatherine A Mazzola*,Catherine Christie,Isabel A Snee,Hamail Iqbal. Atlantoaxial subluxation in the pediatric patient: Case series and literature review. J Neurosci Neurol Disord. 2020: doi: 10.29328/journal.jnnd.1001037; 4: 069-074
-
Intelligent Design of Ecological Furniture in Risk Areas based on Artificial SimulationTorres del Salto Rommy Adelfa*, Bryan Alfonso Colorado Pástor*. Intelligent Design of Ecological Furniture in Risk Areas based on Artificial Simulation. Arch Surg Clin Res. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.ascr.1001083; 8: 062-068
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."